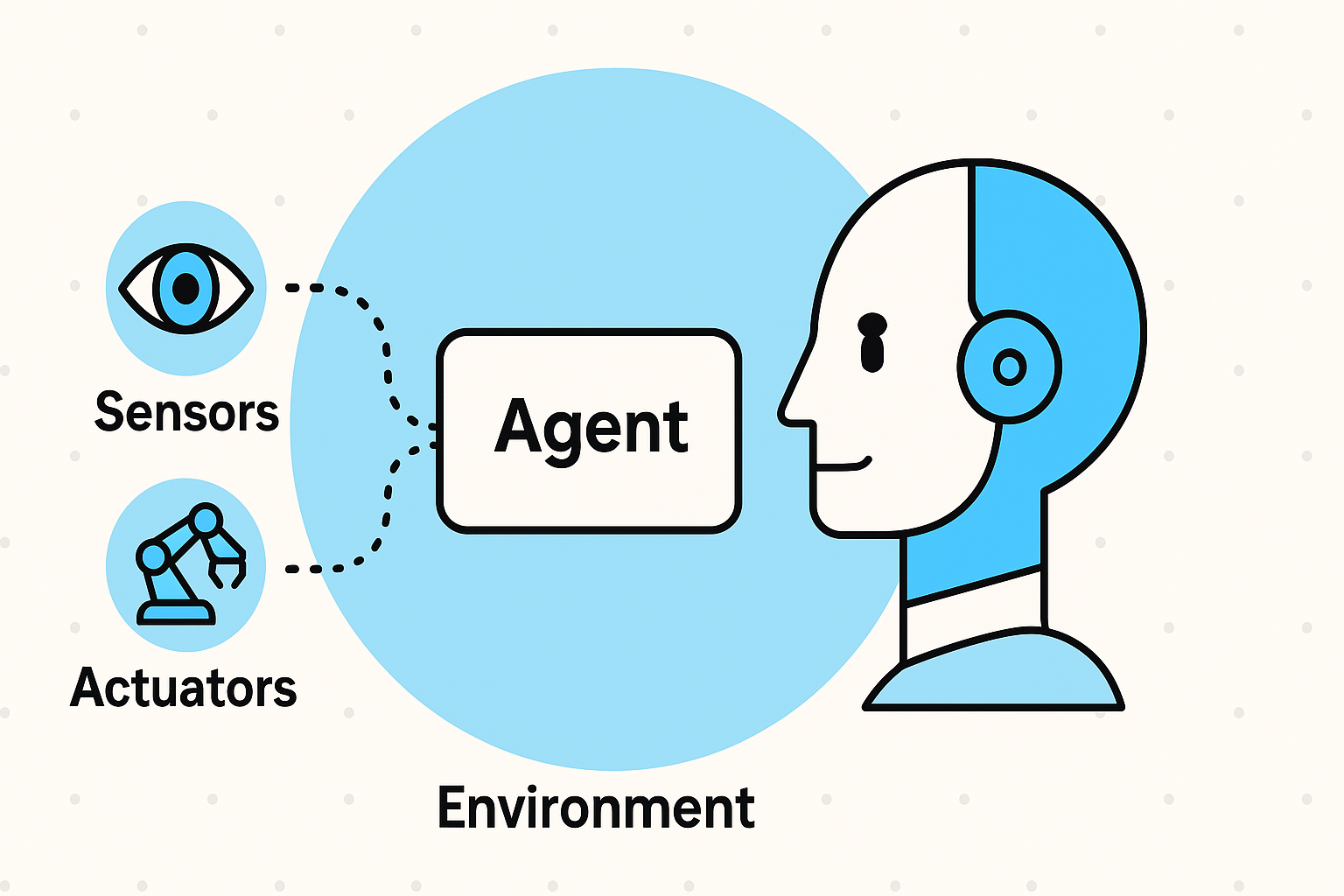
Ever wondered how your Roomba finds its way around the living room, how Siri knows when to tell you it’s raining, or how self-driving cars don’t crash (most of the time)? The answer is simple, yet profound: AI Agents.
They’re the unsung heroes of the AI revolution, the ones doing the perceiving, thinking, and acting. Let’s decode these digital minds.
🤖 So, What Is an AI Agent?
At its core, an AI agent is like a well-trained intern. It:
- Perceives its environment through sensors.
- Thinks or reasons about what to do.
- Acts using actuators to achieve its goals.
Formally, an agent is anything that can perceive its environment through sensors and act upon that environment through actuators.
An AI agent isn’t just reactive. It’s designed to behave rationally — meaning it takes the best possible action given what it knows, not just any action.
🧩 Anatomy of an AI Agent
| Component | Description | Example (in a self-driving car) |
|---|---|---|
| Sensors | Collect information from the environment | Cameras, radar, GPS, LiDAR |
| Actuators | Execute actions based on decisions | Steering wheel, brake, accelerator |
| Agent Logic | The “brain” that decides what to do based on what it senses | Neural networks, rule-based systems |
| Environment | The world the agent interacts with | Road, traffic, weather |
🧠 What Makes an Agent “Intelligent”?
An intelligent agent doesn’t just act — it acts rationally. That means it:
- Chooses the action that is expected to maximize performance.
- Learns or adapts (if it’s a learning agent).
- Has a goal — either explicitly defined (like reaching a destination) or implicitly optimized (like reducing energy consumption).
🚀 Real-World Examples of AI Agents
1. Self-Driving Cars
Sensors detect pedestrians, traffic lights, and road lanes. The agent decides when to turn, stop, or change lanes.
Think of it as a robot driver who never texts while driving.
2. Virtual Assistants (Alexa, Siri, Google Assistant)
They process your voice (sensor), understand the intent (reasoning), and respond or trigger actions (actuators like audio playback or smart home commands).
3. Robotic Vacuum Cleaners
Sensors detect dirt or obstacles. The vacuum decides where to go next, avoiding bumping into the dog.
4. Customer Service Chatbots
They understand user messages, reason through possible solutions, and respond in human-like ways.
🧠 Rationality ≠ Perfection
An AI agent doesn’t have to be perfect — just rational. That means:
- It makes the best choice given what it knows.
- If the agent doesn’t know everything (which it never does), it still strives for the best expected outcome.
- It can make mistakes — but smart agents learn from them.
Just like a chess player who doesn’t know all outcomes, but plays to win.
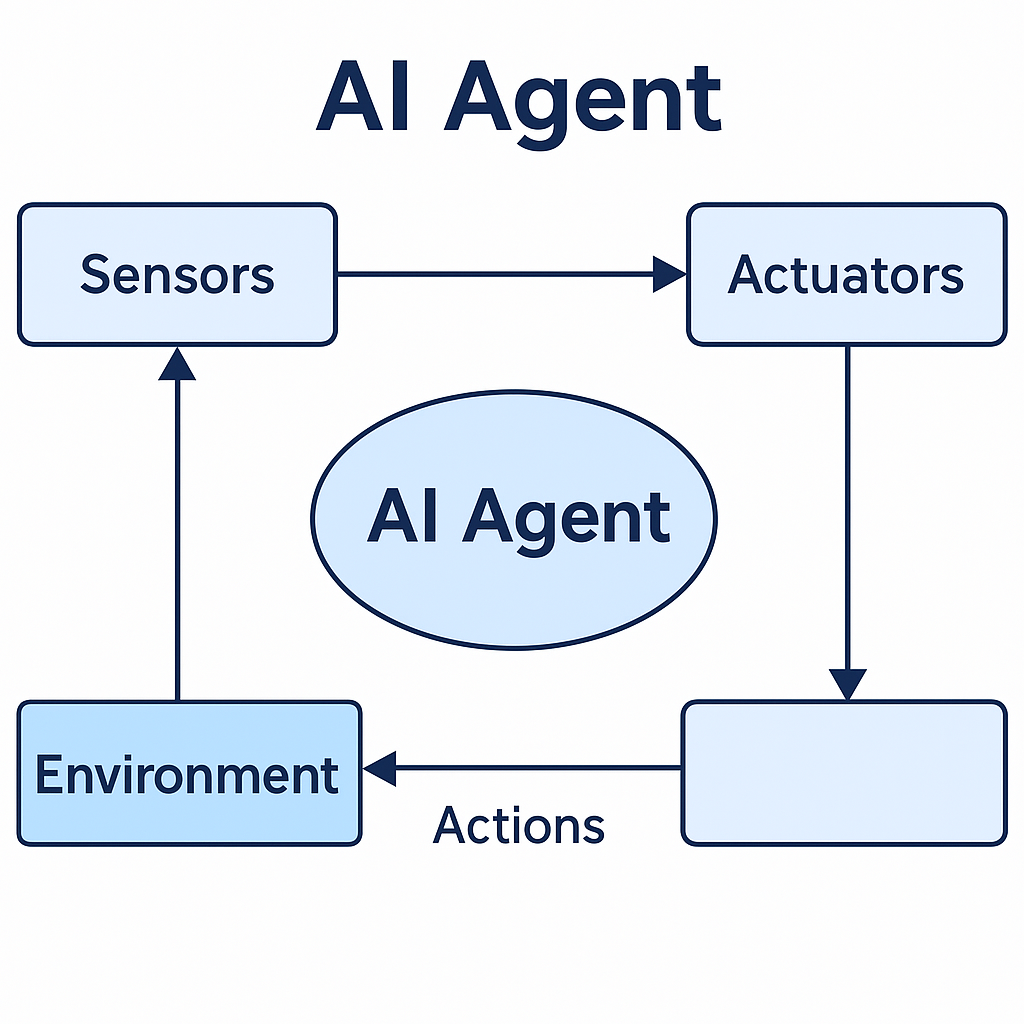
🔄 The Agent-Environment Loop
Here’s how an AI agent typically operates:
- Perceive: Gather data from the environment (via sensors).
- Interpret: Process the data.
- Decide: Choose the best action.
- Act: Use actuators to affect the environment.
- Repeat: Continuously learn and adapt.
Image Source: ResearchGate
🧮 Simple Python Example: Reflex Agent
#python Code
def vacuum_agent(percept):
if percept == "DIRTY":
return "SUCK"
else:
return "MOVE"
# Try it
print(vacuum_agent("DIRTY")) # Output: SUCK
print(vacuum_agent("CLEAN")) # Output: MOVE
A reflex agent acts based only on the current perception — no memory or learning.
💬 Why Should You Care?
AI agents are everywhere. From Netflix recommending your next binge, to drones flying solo, to autonomous investment tools — they are shaping the world.
Understanding them gives you a peek into:
- How autonomous systems work.
- How decisions are made in smart software.
- How to build your own agents (even as a beginner).
✅ Key Takeaways
- An AI agent perceives, decides, and acts in an environment.
- It can be simple (like a reflex bot) or complex (like a self-learning autonomous car).
- It always strives to be rational — choosing the best action based on current knowledge.
- They’re everywhere — in tech, health, finance, gaming, and even your fridge!
🔗 Further Reading & Resources
👉 Up Next in the AI Agent Series
Now that you understand how AI agents think, act, and learn, let’s take it a step further. In our next article, we explore the different types of AI agents—how they behave, why they matter, and where you’ll see them in action.